Blood Sugar Test Types, Average Levels & Diabetes
Jun 04, 2020
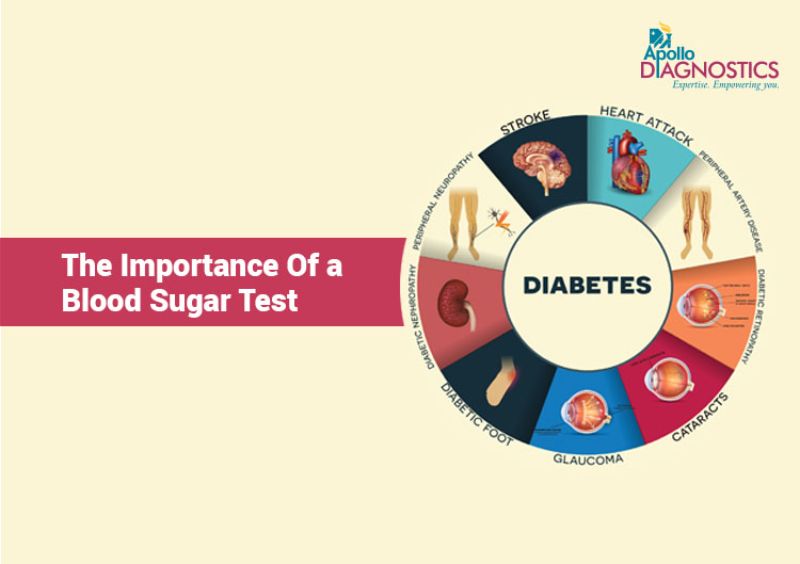
A Blood Sugar Test / Blood Glucose Test is done to check the levels of glucose in the body. Also known as blood sugar, glucose is the simplest of carbohydrates – our energy providers. It is a simple sugar that is absorbed into the bloodstream and is carried to all the cells in the body, which in turn use it to produce energy.
What causes blood sugar levels to change?
Glucose levels are controlled by insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. If the pancreas is unable to do this due to some reason, problems occur.
Other than this, high blood sugar (hyperglycaemia) may result from physical inactivity, consumption of carbohydrate-rich food, hormonal changes, stress, kidney issues, hyperthyroidism and pancreatitis, among others.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) is caused by excessive activity, skipping meals, alcohol consumption, or more seriously, hypopituitarism, hypothyroidism, liver disease, insulinoma (a pancreatic tumour), and Addison’s disease.
Though the reasons are various, blood sugar tests are not used as conclusive proof of these disorders. However, one certainty that follows abnormally high blood sugar levels is diabetes mellitus.
Hyperglycaemia and diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is the term that is most commonly associated with high blood sugar. Blood sugar tests are usually done to diagnose this disorder.
Type 1 diabetes, mostly seen in children and adolescents, is a chronic condition in which the beta cells of the pancreas are erroneously killed by the body’s immune system. Thus, the pancreas is unable to release insulin into the body, and the glucose, which is no longer being converted into energy, accumulates in the blood.
Type 2 diabetes occurs mostly in adults whose bodies do not produce enough insulin, or cannot make proper use of the insulin produced.
In addition, pre-diabetes is a condition that reveals a high risk for diabetes. This, like diabetes, is determined according to the blood glucose levels.
What are the various kinds of tests?
Fasting blood sugar test is taken on an empty stomach, right after waking up. A normal result would range between 70 and 99 mg/dl.
Random blood sugar test is taken at a random time during the day, and any reading up to 125 mg/dl is considered normal. This, however, varies according to what was last consumed and when.
Post-prandial blood sugar test is done two hours after a proper meal. If glucose levels are normal, the reading should not go beyond 140 to 145 mg/dl.
Oral glucose-tolerance test (GTT) is administered by drawing a blood sample, making the person drink a glucose solution, and following up by taking more samples after an hour, and an hour later. This is done to check the body’s reaction to the glucose.
The A1C test, also known as the glycohaemoglobin test, gives a reading of the average levels of blood glucose over the past three months. It is based on the principle that glucose attaches to haemoglobin in the blood, and therefore measures the amount of glucose bound to the haemoglobin in the RBCs, which usually live for three months. A normal reading ranges from 4% to 6%.
What readings would indicate diabetes?
Two fasting blood sugar tests taken consecutively, giving a result higher than 125 mg/dl.
A random blood sugar test showing glucose levels higher than 200 mg/dl.
A GTT indicating levels higher than 200 mg/dl at two hours.
An A1C test that reads equal to or more than 6.5% glucose in the haemoglobin.
Any value that falls between the higher limit of the normal range, and the lower limit of the abnormal range, indicates pre-diabetes, and a cautionary lifestyle is advised at this stage itself.
Watching every step
While not all factors are under our control, lifestyle-induced hyperglycaemia (and consequently, diabetes), may be prevented by making changes in activity levels and dietary habits. If the risk is obvious, a blood sugar test should be done straightaway so that a diagnosis can be made before it is too late. You may find reliable testing procedures and accurate results at your nearest Apollo Diagnostics centre.
Related Blog Post
Blog Categories
- Child Health
- Mens Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Health
- Health Myths & Facts
- Fitness
- Nutrition/Recipes
- Remedies
- Weight Management
- Stress Management
- Health Supplements
- Addiction Management
- Disease Management
- Allergy
- Anemia
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Blood Pressure
- Cancer
- Deficiencies
- Dengue/Malaria/Chikungunya
- Diabetes
- Eye Problems
- Heart Diseases
- Hepatitis
- HIV/AIDS/STD
- Hormonal Imbalance
- Infection/Flu/Viral
- Kidney
- Liver
- Menstrual Problems
- Pregnancy
- Skin & Hair Problems
- Stomach Ailments
- Thyroid
- Others
- Health Checkups
- Diagnostics/Pathology
- Lifestyle & Wellness
- Covid
- Medical Tests
- Cholesterol
- Health Tips
- Parent Care/Old Age
- Lungs
- Food Intolerance









